Diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus are two different diseases. Diabetes mellitus is a disease that affects how the body uses sugar. Diabetes insipidus is a rare condition that causes the body to produce too much urine.
Difference Based on Disease Presentation
People with diabetes mellitus have high blood sugar levels because their bodies cannot use sugar properly. On the other hand, people with diabetes insipidus have high urine levels because their kidneys cannot hold onto water. This can lead to dehydration and a potentially dangerous amount of chemicals in the blood (called electrolytes).
People who suffer from diabetes mellitus might feel thirsty even if they do not drink anything or frequently urinate throughout the day. People who suffer from diabetes might urinate more often than usual. They also tend to feel thirsty and drink a lot of fluids.
According to the experts at Tandem Diabetes, symptoms and signs of type 2 diabetes mellitus may include: Blurred vision, feeling very tired, increased thirst and urination, and weight loss.
Symptoms of type I diabetes mellitus (juvenile-onset) may include:
- Extreme thirst and hunger even after eating
- Frequent urination
- Weight loss
- Drowsiness or lethargy
- Dry skin and mouth
- Fruity-scented breath
- Nausea and vomiting
- Feeling very tired
People with diabetes mellitus may lose weight without trying because their bodies break down fat for fuel instead of glucose (the body’s primary energy source). People with diabetes insipidus will not lose weight because they urinate too often.
Difference Based on Etiology

People with diabetes mellitus have a problem with their pancreas, which is the organ that makes insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps the body use sugar for energy. People with diabetes insipidus do not have a problem making or using insulin. Instead, they have a problem with the pituitary gland, a small gland in the brain. The pituitary gland controls how much urine the kidneys make.
People with diabetes mellitus are at risk for other health problems such as heart disease, stroke, and blindness. People with diabetes insipidus do not have these same risks. Cholesterol levels and blood pressure are usually normal in people with diabetes insipidus but slightly high in persons with diabetes mellitus.
Diabetes mellitus is a lifelong disease, while diabetes insipidus is a rare condition that can go away on its own. People with diabetes mellitus must carefully monitor their food intake and blood sugar levels. People with diabetes insipidus do not have to be as careful about what they eat or drink. They also do not have to check their blood sugar levels as often.
Difference Based on Management

There is no known cure for diabetes mellitus, but people can manage their symptoms with insulin, diet, and exercise. There is no known cure for diabetes insipidus either. However, it may go away on its own.
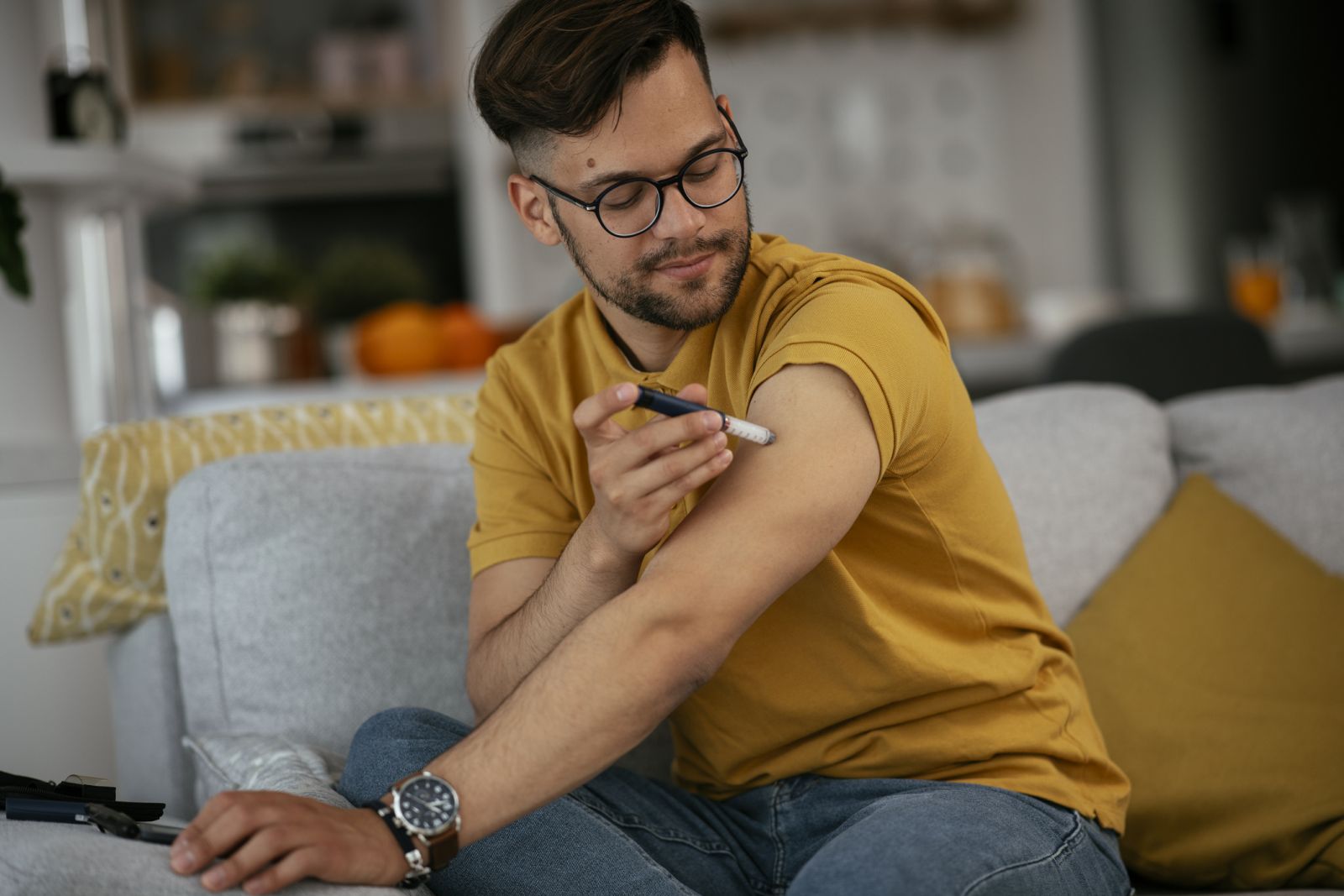
People with diabetes mellitus might need to take insulin shots, while diabetes insipidus usually does not require medication. However, some people with diabetes insipidus may need to take desmopressin (DDAVP) to help their bodies retain water. They also have to drink plenty of fluids and watch their salt intake because too much salt can worsen the condition.
In summary, both diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus are endocrine disorders. Although both diseases share the same initial name, each disease has different causes, symptoms, management, and pathology.
Related Searches :
diabetes mellitus, diabetes mellitus definition, diabetes mellitus ppt, type 2 diabetes mellitus, complications of diabetes mellitus, types of diabetes mellitus, what is diabetes mellitus, diabetes mellitus causes, causes of diabetes mellitus
diabetes mellitus symptoms, gestational diabetes mellitus, difference between diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus, symptoms of diabetes mellitus, definition of diabetes mellitus, pathophysiology of diabetes mellitus, health education for diabetes mellitus, type 1 diabetes mellitus








